The juicy, delectable interior of rambutan is enticing. Vitamins, carbohydrates, calcium, magnesium, and potassium are all abundant in fruits. Research has shown that the antioxidants found in rambutans' rind and aril can prevent cancer cell growth.
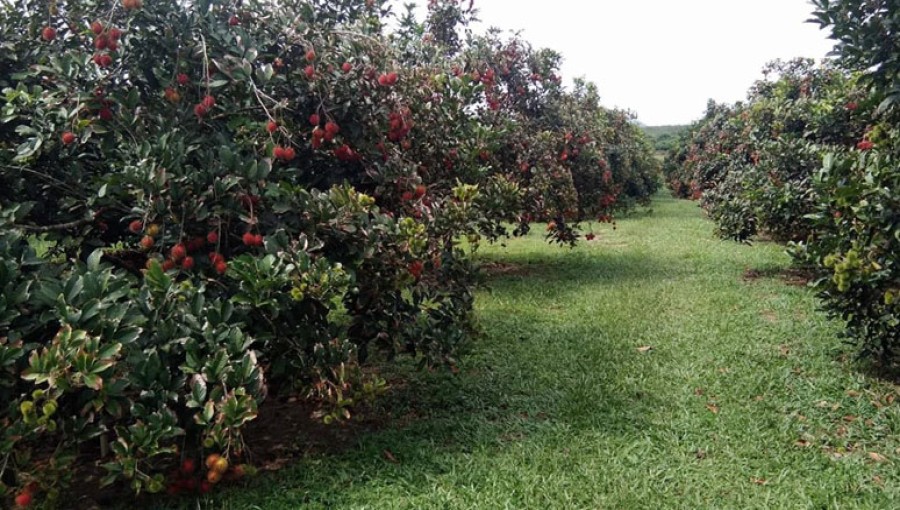
Farmers have already shown that it is possible to enhance Bangladesh's agroclimatic conditions to support the growth of Rambutan, one of the most well-liked fruits in Southeast Asia.
We may cultivate rambutan trees as ornamental plants in our nation.
The seed's luscious, mouthwatering inside is appealing. Fruits are a great source of vitamins, carbohydrates, calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Studies have demonstrated that the antioxidants in the rind and aril of the rambutan can stop the formation of cancer cells.
.jpeg)
Warm, tropical climates are ideal for rambutan growth. Important factors to take into account include a suitable climate and increased humidity. It also needs a minimum of 150 centimetres of evenly distributed annual rainfall. Even at elevations of up to 800 feet above sea level, the trees flourish.
For best development, temperatures between 22 and 35 degrees Celsius are ideal. On the other hand, the minute changes in the climate would not significantly impact its growth and production. Loamy soils with a high organic content and good drainage are ideal for growth and production. Maintaining the soil's balance between its acidic and alkaline properties (pH value 4.5 to 6.5) is important.
Transmission
Nephelium leppaceum is the scientific name for the rambutan, a member of the Sapindaceae family. The term "rambutan" originates from the Malay word "rambut," meaning "hair." The fruit has an oval or circular form. Usually, a cluster has five to twenty fruits. The leathery outer shell is frequently red or yellow in hue.
Because the two types of blooms have different sexes, rambutan cultivation does not need seedling propagations. Rather, the best way to produce high-quality plants is by budding. After three years of healthy care, it begins to blossom and produces at its peak six to eight years later.
- Depending on the weather, the best distance between two saplings is 40 feet, however, this might vary from location to location.
- Up to 35 seedlings might be planted in an acre of land.
- Fill the one-meter-square trenches with topsoil mixed with three pots of compost or well-decomposed cow dung manure, and one kilogramme of rock phosphate each pot. After that, set the plant with its buds united above the dirt.
- The planting hole should be surrounded by a small handful of soil-mixed rock phosphate and compost, or dried cow dung manure. After six months, further fertiliser can be applied, but only after the new leaf flush has appeared and grown.
- During the dry season, effective irrigation is crucial. Weeds should be periodically pulled to keep the orchard tidy. Water suckers and dried branches need to be removed regularly.
Rambutan grows long and straight, therefore it's best to prune it early. Trim the main stem at 2.5 feet after the budding reaches 4 feet. Allow three or four limbs to grow out of each new sprout in different directions.

These limbs will eventually generate primary, secondary, and tertiary branches, which will give the tree a semi-elliptic shape. The best yield will be attained in this way. This planting technique can be finished in two years.
Application of Fertiliser
A plant that responds well to fertiliser is the rambutan. Only when the new flush of leaves has sprouted and matured may fertilisers be applied. It works well to add 5 kg of compost or cow dung manure mixed with soil.
- Mulching has been proven to be a very successful method of preserving moisture. "Jeevamritham" spraying may encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria. Additionally, it will aid in the plants' drought resistance. Applying cow dung manure to enhance Trichoderma is beneficial.
- Fill each of the one-meter-square trenches with one kilogramme of rock phosphate, three pots of thoroughly decomposed cow dung manure or compost, and topsoil. Plant the plant after the bud union is above the soil's surface.
- Fill the area surrounding the planting hole with a small amount of soil-mixed rock phosphate and compost or dried cow dung manure. Additional fertilisers can be sprayed after six months, but only after the new leaf flush has emerged and grown.
- Adequate irrigation is essential during the dry season. To maintain the orchard tidy, regularly remove weeds from it. Regular removal of dry branches and water suckers is recommended.
The process of pollination
February through April is when flowers bloom. Selecting the appropriate irrigation technique depends on the age and yield of the trees. The production of rambutan necessitates the presence of honey bees due to its cross-pollinated nature. After pollination, the first phase of fruit production lasts for three weeks. We might employ fresh strategies to restore its quality after three weeks.
When the trees are about to blossom, add 25 grammes of boron for little trees and 50 grammes for larger trees, blended into the soil. The utilisation of Pseudomonas fluorescent liquid formulation (6 ml/l) is beneficial in managing fruit drop and producing fruits of superior grade.
Fruiting plants can get 200 g of 18 complexes as well as 100 to 250 g of muriatic potash and 4-5 g/l of potash sulphate administered topically (1 litre per tree). Fruit drop is significantly reduced when developing fruits are sprayed with 1g/l wettable sulphur. Numerous things, such as a deficiency in micronutrients and alterations in the oxin-cytokinin hormone, can cause fruit drop.
Applying foliar spray after using leaf tissue analysis to determine the proper ratio of microelements is efficient. An efficient way to stop any kind of fungal infestation is to spray sulphur solution (3g/l).
High-quality trees in orchards have two types of flowers. Ninety-five percent of these flowers are bisexual in structure and functionally female. Some bisexual flowers require a shift in pattern from their male counterparts to their female counterparts to increase productivity. For this process, a 10% cluster of flowers has to be found and noted.
.jpeg)
Some of the buds in this particular cluster open simultaneously, while the remaining buds stay in the buds. The best time to spray Superfix solution is at that time.
Combine one before 9 a.m.
two litres of water and one millilitre of Superfix, thoroughly mixing. Six days later, the blossoms may have changed into male flowers and the stamens would have emerged; this window of time provides for higher yields. Such an important procedure has to be given the highest consideration to provide fruits of the highest calibre.
Termite Management
Generally speaking, well-maintained rambutan trees are immune to pests. Keeping a 40-foot gap between plants is an effective way to safeguard them. The main hazards to plants include dry branches, mealybug attacks, beetle attacks, and caterpillars that consume leaves. Eliminating the impacted branches is a practical method to stop the spread. Neem-based formulations can be used to suppress leaf-eating caterpillars in the event of a severe assault. Mealybug infestations can be effectively managed using verticillium.
end//voice7news
A global news agency.




























Comment: