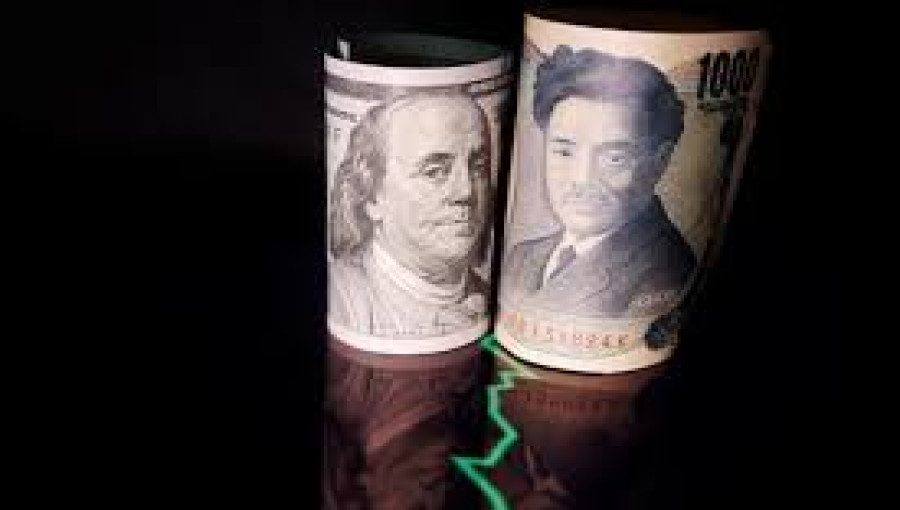
NEW YORK/LONDON/SINGAPORE, Dec 20 (Reuters/V7N) – The U.S. dollar remained near its two-year high on Thursday, fueled by recent developments surrounding central bank decisions. The Federal Reserve's decision to cut interest rates, combined with a slower-than-expected pace of monetary easing projected for 2025, helped maintain upward momentum for the greenback. At the same time, the Japanese yen weakened against the U.S. dollar after the Bank of Japan (BoJ) chose to keep interest rates unchanged, despite a challenging domestic economic backdrop.
U.S. Dollar Performance
The U.S. dollar edged higher, recovering from early-session losses. The uptick was supported by the latest U.S. economic data, which revealed that the country’s economy expanded at a 3.3% annual rate in the third quarter of 2024. This stronger-than-expected reading on GDP growth suggests resilience in the U.S. economy and bolstered expectations of the Fed's cautious approach to rate cuts going into 2025.
The Federal Reserve’s announcement earlier this week signaled a much slower pace of monetary policy easing in the upcoming year. This cautious approach contrasts with earlier expectations for a more aggressive reduction in rates and has provided further support for the dollar. Analysts have interpreted the Fed's stance as a reflection of ongoing concerns about inflation and labor market tightness, keeping the U.S. dollar attractive to investors seeking stability.
Yen Weakens After BoJ Holds Rates Steady
Meanwhile, the Japanese yen weakened against the dollar, dropping to a multi-week low, after the Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) decision to hold interest rates steady. The BoJ’s policy divergence with the Federal Reserve has been a key factor driving the yen’s depreciation. The Japanese central bank’s ongoing accommodative stance, despite pressures in the domestic economy, contrasts with the Fed's relatively hawkish approach.
The BoJ’s policy decision reflects its cautious outlook on Japan’s economic recovery, with inflationary pressures remaining persistently low. The yen’s weakening is in line with broader trends seen over the past several months, as the difference in interest rates between the U.S. and Japan continues to widen.
Economic Data and Market Impact
The stronger-than-expected GDP report for the U.S. added to investor confidence that the U.S. economy remains resilient despite global challenges. The 3.3% annual growth rate in Q3 2024 exceeded the market consensus of 2.9%, suggesting robust consumer spending and investment.
This economic performance has reinforced expectations that the Federal Reserve will maintain its policy stance through 2025, supporting the dollar’s upward trajectory. Meanwhile, the yen’s weakness against the dollar reflects the BoJ’s reluctance to tighten policy amid Japan’s economic challenges, creating a continuing divergence between the two major currencies.
Market Outlook
Looking ahead, the outlook for the U.S. dollar remains positive as the Fed signals a gradual approach to monetary easing. The yen’s performance, on the other hand, will continue to be shaped by the BoJ's policy decisions and Japan’s economic recovery, with the currency likely to face continued pressure in the near term.
Market participants will closely watch future economic data from the U.S. and Japan, including inflation figures and employment reports, to gauge the direction of monetary policy. The dollar’s strength and the yen’s weakness may persist as long as the gap between U.S. and Japanese interest rates remains wide.
Summary
- U.S. Dollar: Near two-year high, supported by strong Q3 GDP and Fed’s cautious monetary easing outlook.
- Japanese Yen: Weakens after BoJ’s decision to keep rates steady, continuing divergence from the U.S. monetary policy.
- U.S. GDP: Strong 3.3% annual growth rate in Q3 2024, signaling economic resilience and supporting the dollar.
- Fed vs. BoJ: Divergence between U.S. and Japanese monetary policies continues to impact currency dynamics.



























Comment: