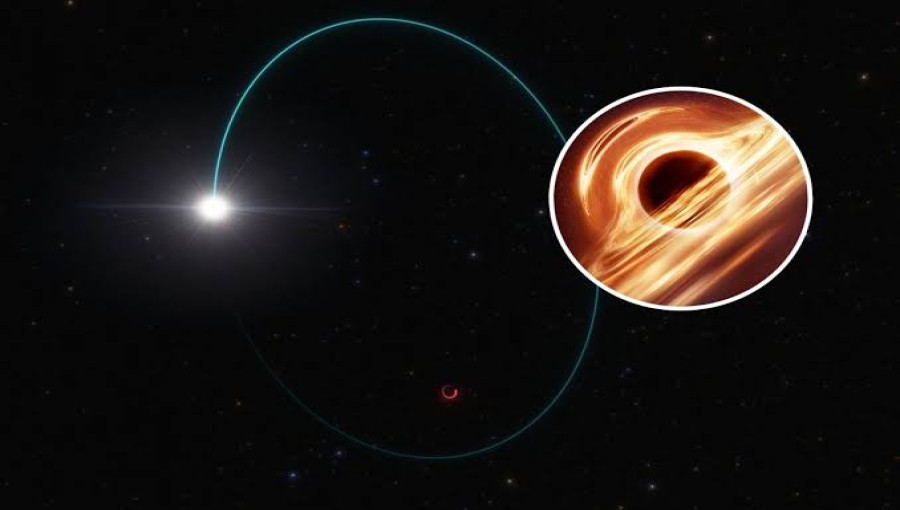
French researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery, identifying what is believed to be the largest black hole in the galaxy. The colossal black hole, named Gaia BH3, boasts a mass a staggering 33 times heavier than that of the Sun. The findings were reported on Wednesday by US news media outlet CNN.
The discovery of Gaia BH3 was made possible through the meticulous analysis of data collected by the European Space Agency's Gaia mission. The Gaia telescope, renowned for its precision, played a pivotal role in this groundbreaking observation.
Utilizing the Gaia telescope's advanced capabilities, astronomers were able to pinpoint the exact position of stars in the sky with unparalleled accuracy. This invaluable data provided insights into the masses, orbits, and even the presence of invisible companions of celestial bodies.
Gaia BH3 was identified within the Aquila asteroid cluster, situated approximately 2,000 light-years away from Earth. The black hole's immense size and proximity to our planet make it a remarkable object of study for astronomers seeking to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos.
The discovery of Gaia BH3 marks a significant milestone in our understanding of the universe's most enigmatic phenomena. As researchers continue to delve deeper into the cosmos, revelations such as this serve to expand our knowledge and reshape our perception of the cosmos.




























Comment: