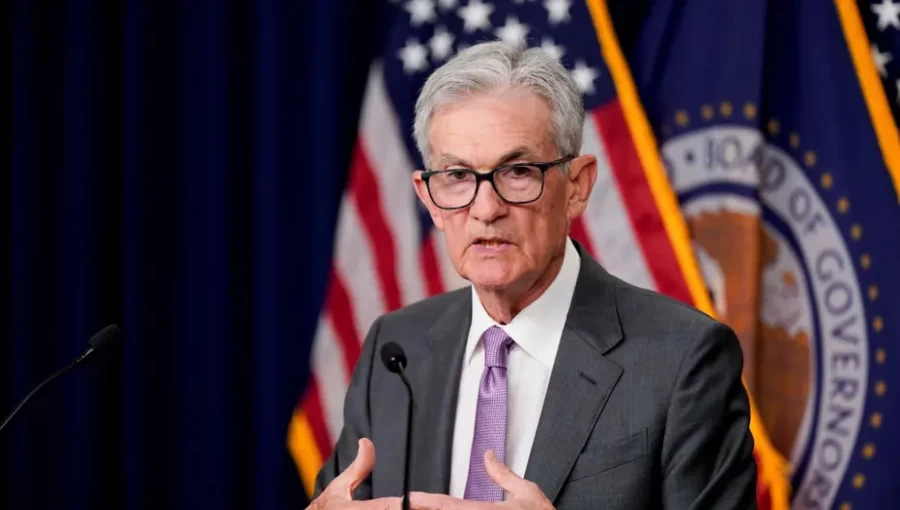
Sept 19, V7N - On September 18, 2024, the U.S. Federal Reserve announced a larger-than-usual half-percentage-point cut in interest rates, marking the beginning of a series of anticipated reductions. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell stated that this decision reflects the central bank's commitment to maintaining a low unemployment rate as inflation continues to ease. The benchmark policy rate has now been adjusted to a range of 4.75% to 5.00%. Powell expressed satisfaction with the decision, emphasizing the need for proactive measures to support the labor market.This rate cut is notable not only for its size but also because it marks the first dissent from a Fed governor since 2005, with Governor Michelle Bowman voting for a smaller quarter-point reduction. Analysts view this dissent as indicative of Powell's determination to initiate the easing cycle decisively. The Fed's move is described as a "recalibration" in response to the significant decline in inflation since last year, with Powell highlighting the importance of acting before any potential weakening in the job market occurs.
Economic Projections and Market Reactions
In addition to the immediate rate cut, Fed policymakers projected further reductions, anticipating another half-point cut by the end of this year and a total decrease of one percentage point by the end of 2025. This shift in monetary policy signals the Fed's growing confidence in the economy's resilience, despite inflation currently being slightly above the central bank's 2% target.The announcement initially elicited a muted response from presidential candidates, with Vice President Kamala Harris welcoming the news while Republican nominee Donald Trump suggested that the size of the cut indicated economic trouble. Powell maintained that the economy remains strong, citing stable unemployment rates and positive job market indicators. However, he acknowledged the need for caution, noting that changes in monetary policy take time to manifest in the economy.
Implications for the Future
The Fed's decision to cut rates comes after a prolonged period of maintaining higher rates to combat inflation, which peaked at a 40-year high in 2022. Powell refrained from declaring victory over inflation but noted that conditions are aligning with the Fed's dual mandate of maximum employment and stable prices. As the central bank navigates this transition, market reactions included a brief uptick in U.S. stocks, followed by a decline, while the U.S. dollar strengthened against other currencies.Overall, the Fed's actions represent a significant pivot in U.S. monetary policy, with implications for economic growth and employment as the nation approaches the upcoming presidential election.
END/WD/RH/
























Comment: