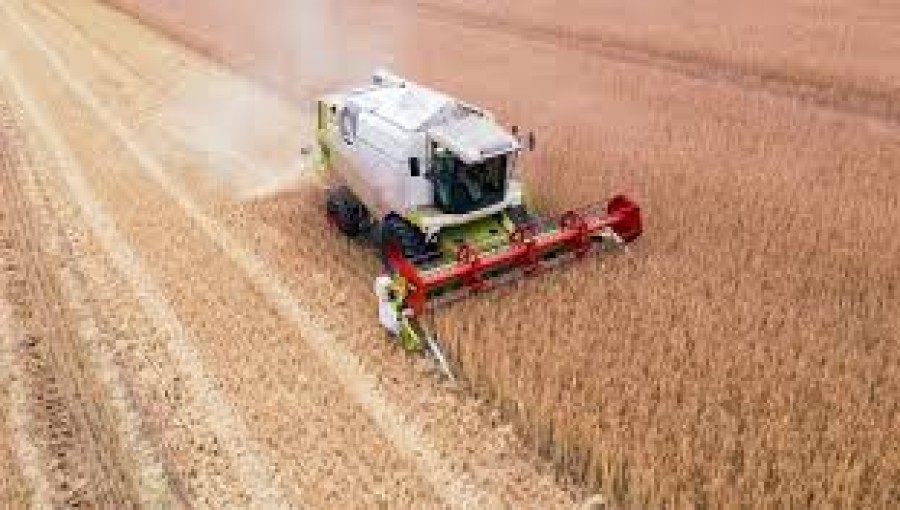
The use of hydrogen in agriculture presents a promising avenue for sustainability in food production. By replacing diesel or gasoline with hydrogen fuel cells in farm equipment, farmers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, with water being the only byproduct. Additionally, hydrogen can be utilized to create environmentally friendly fertilizers and pesticides, contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
Furthermore, storing food in a hydrogen atmosphere has been shown to extend shelf life, and there are pilot projects exploring the use of hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity on farms. Despite the potential benefits, challenges such as infrastructure, costs, and safety must be addressed for widespread adoption.
Hydrogen's application in agriculture extends beyond fueling machinery; it can also enhance crop yields and soil health. Studies suggest that hydrogen as a fertilizer or crop treatment can improve plant growth, fruit production, and soil microbial activity. Additionally, hydrogen enables the production of greener fertilizers like ammonia, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional fertilizer manufacturing processes reliant on fossil fuels.
However, the transition to hydrogen farming may face resistance from some consumers concerned about the use of alternative chemicals in food production. Nevertheless, with growing awareness of the environmental benefits and potential improvements in crop quality, hydrogen farming could play a significant role in promoting sustainable agriculture in the future.





























Comment: