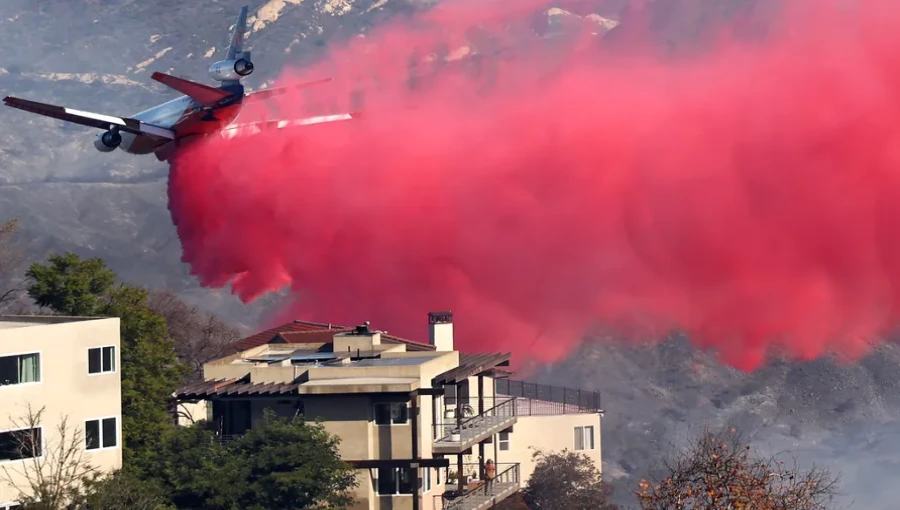
Los Angeles, Jan 14, (V7N) - Authorities battling a series of large wildfires in the Los Angeles area have employed a bright red fire retardant to control the flames, leading to dramatic images of the material blanketing homes, cars, and streets. As large tankers drop tons of the retardant over swaths of Southern California, questions have emerged about its composition, how it works, and its environmental impact.
What is the fire retardant made of?
The fire retardant, known as Phos-Chek, has been used for over 50 years. It primarily consists of agricultural salts that alter the way fire burns, decrease its intensity, and slow its spread. The mixture also includes water, which is available as wet or dry concentrates depending on fire response needs.
Why is fire retardant red?
The vibrant red color comes from iron oxide (rust), making the retardant easily visible from the air. The color fades naturally over time due to weathering, rain, or other environmental factors.
How does fire retardant work?
When heated, the retardant prevents the cellulose in plant matter from fueling the fire. It emits water vapor, cooling the fire and starving it of fuel. A black carbon coating left behind helps insulate and restrict airflow, making it easier to control the fire.
Is fire retardant safe?
Phos-Chek is USDA-approved and meets environmental safety standards. It does not contain substances linked to cancer or reproductive harm. However, there is a 300-foot buffer required between the retardant and waterways due to potential risks to aquatic life. Although the USDA allows exceptions during emergencies, any intrusion must be reported and managed. A study from UCLA raised concerns about heavy toxic metals in fire retardants, but Phos-Chek's manufacturer has disputed the findings.
END/SMA/NYC/AJ/






























Comment: