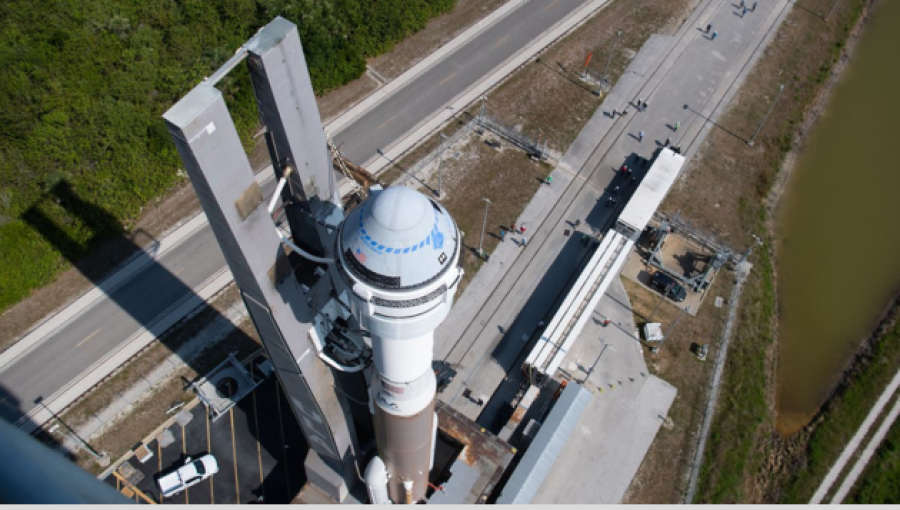
Google has introduced significant updates to its two-factor authentication (2FA) process, aiming to simplify and enhance security measures for users safeguarding their accounts. The revamped process, referred to as two-step verification (2SV), offers users more flexibility and options to strengthen the security of their Google accounts.
The key improvement lies in providing users with the choice to initiate their 2FA setup directly with more secure methods, such as authenticator apps or physical security keys. Previously, users were required to provide a phone number before adding an authenticator app, but this mandatory step has now been eliminated.
While SMS verification codes have been a standard method for enhancing account security, they are considered less secure compared to alternatives like authenticator apps. With Google's update, users can bypass phone number verification and opt for more secure options, such as time-based codes generated by authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, or utilizing physical security keys.
Google has streamlined the process of linking security keys, offering two methods: registering a FIDO1 credential on the key or setting up a passkey. However, it's important to note that passkey setups may still necessitate standard password login for Workspace accounts, depending on organizational settings.
Furthermore, Google has adjusted the process for turning off 2FA. Previously, disabling 2FA would remove all associated security measures, including backup codes, authenticator app links, and linked phone numbers. Now, these additional security layers remain intact even after 2FA has been disabled.
These updates are being rolled out to both Google Workspace subscribers and users with personal Google accounts, reflecting Google's commitment to enhancing account security across its user base. With these improvements, users have more control over their account security, with a range of options to choose from to suit their preferences and needs.




























Comment: