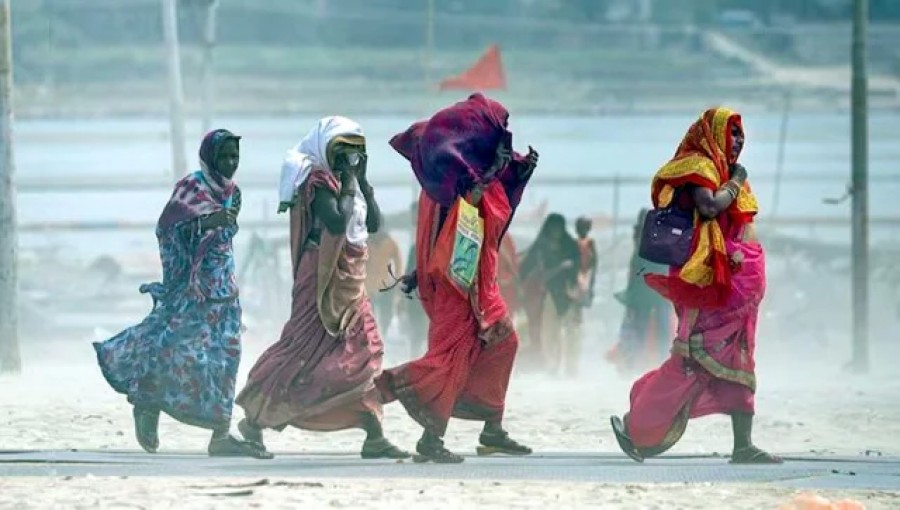
As temperatures soar across India, concerns mount over the looming threat of heatwaves gripping various states in May. The Central Meteorological Department of India has issued warnings, predicting five to eight extreme heatwaves in South Rajasthan, West Madhya Pradesh, Marathwada, and Gujarat.
Last April, West Bengal and Odisha experienced unprecedented heatwaves, with temperatures reaching historic highs. Odisha endured a scorching heatwave for 16 consecutive days, marking a stark departure from the past nine years. The absence of Kalbaisakhi, or pre-monsoon storms, exacerbated the heat, with Kolkata and neighboring districts grappling with rising mercury levels.
Experts attribute the prolonged heat to a variety of factors, including deforestation and urbanization. The encroachment of concrete structures impedes the natural exchange of hot and cold air, trapping heat in the environment. India's Central Meteorological Department has warned of above-normal temperatures persisting into May, albeit with a gradual decline in heatwave intensity.
El Nino, a climatic phenomenon characterized by warmer-than-average sea temperatures, has also contributed to rising temperatures. Reduced thunderstorm activity and anti-cyclonic circulation along India's southeast coast exacerbate the heatwave conditions.
The sweltering conditions have not spared Kerala, where at least two fatalities have been reported due to soaring temperatures. Additionally, the state grapples with dwindling river water levels, exacerbating the impact of the heatwave.
In contrast, the northern region of Kashmir experienced heavy rainfall and snowfall, triggering landslides in several areas. Sonmarg, a picturesque region, witnessed mudflows cascading down snow-covered mountains, prompting evacuations. Landslides also forced the closure of the vital Jammu-Srinagar highway, disrupting travel between Kashmir and the rest of India.
As India braces for continued heatwave conditions, authorities urge residents to take precautionary measures to mitigate the risks associated with extreme temperatures.



























Comment: